Abstract Entity.
A CDS abstract entity defines the type attributes of a CDS entity without defining a database
object.
CDS abstract entities can be used as
- data types whose type attributes go beyond the regular DDIC structures in the ABAP Dictionary
- prototype definitions of data models without being created as instances of a data object.
Example:
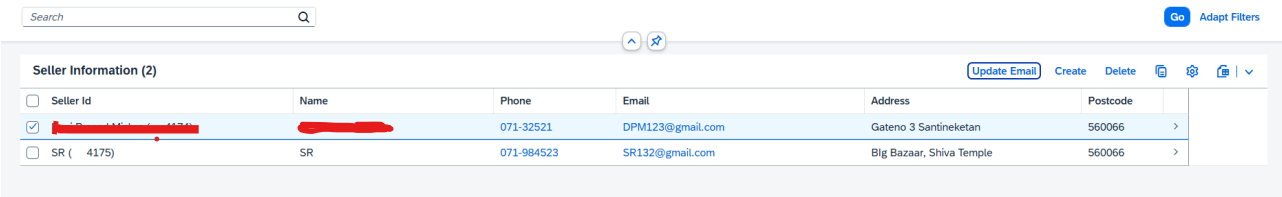
Administrators can update a seller’s email via a “Update Email” button in the Seller Details form.Clicking the button opens a popup modal displaying the current email, an input field for the newemail, and an optional reason for the update. Validation ensures the new email has a proper format and is not duplicated. On save, an abstract entity processes the update, and the system
records the change for compliance.
Create a CDS abstract entity
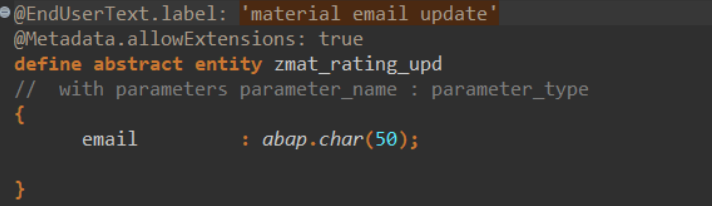
Add it using action in Behavior definition.
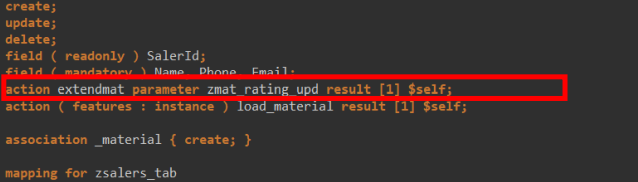
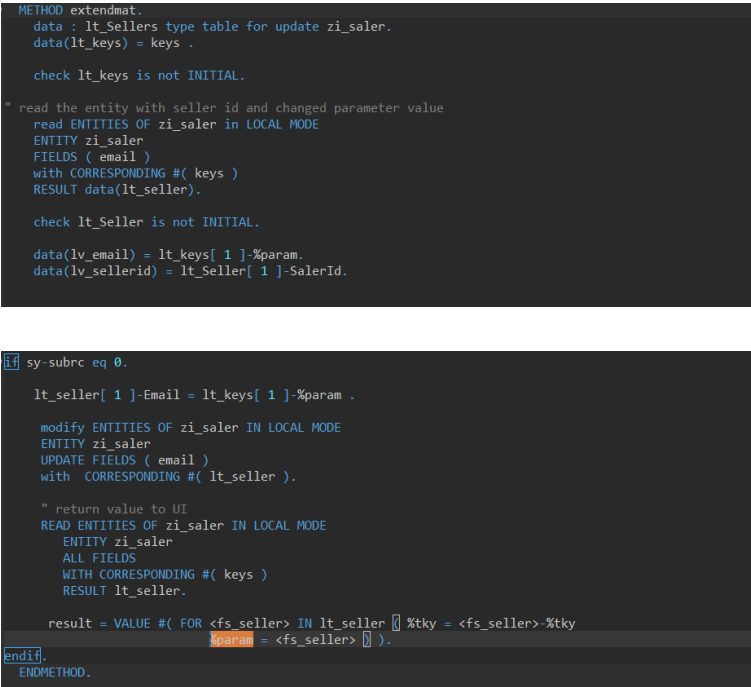
Implement the method and modify the field.
In Preview Screen → Before email update
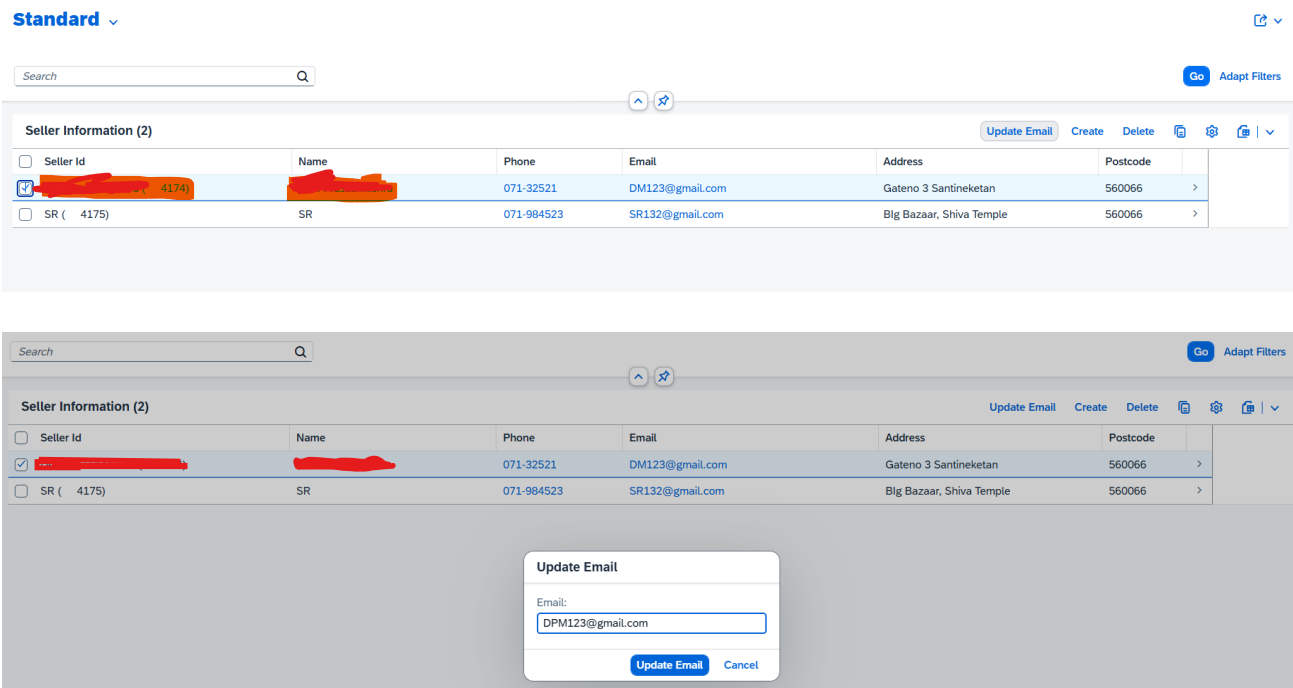
Email field updated
Conclusion:
Abstract entities in RAP applications provide a powerful framework for enhancing modularity, scalability, and reusability by encapsulating shared business logic and ensuring consistent behavior across root entities. This is particularly evident in scenarios like updating a seller’s email, where an abstract entity centralizes the handling of operations such as validation, transformation, and automated updates. The use of a popup modal for updates, paired with the abstract entity’s logic, ensures a user-friendly experience, streamlined workflows, and systemwide synchronization. This approach aligns with clean architecture principles, resulting in robust, maintainable, and adaptable applications capable of efficiently meeting current and future requirements.