The managed save sequence is a key concept in the RAP (Restful Application Programming) framework used to handle persistence operations for entity instances in ABAP. It automates the process of saving changes made to
an entity while allowing customization when needed.
Key Components of the Managed Save Sequence
- Standard Behavior
- Automatically saves changes made to entity instances in the database.
- Ensures consistent data persistence without requiring additional coding.
- Steps in the Sequence
- Data Validation: Validates the modified instance to ensure data integrity.
- Data Modification: Updates or inserts the instance data into the database.
- Lifecycle Management: Manages the lifecycle events triggered during the save process.
- Post-Save Actions: Completes any final actions after the data persisted.
- Customizing with Extra Save
- The extra save feature allows adding additional logic to the save process, such as logging changes or triggering external services.
- Developers can implement additional steps using the save_modified method in a saver class.
- Change Tracking
- Logs changes made to an instance, such as modified fields or newly added data.
- These changes can be written to a log table for auditing or debugging purposes.
Unmanaged save is ideal when the default save logic in the RAP framework (managed save)cannot handle specific business requirements. It gives developers full control over how data persisted, enabling customization for complex scenarios like:
Custom Table Structures: When data is stored in unconventional formats or across multiple tables.
Advanced Integrations: When saving data involves external APIs or systems.
Complex Logic: For operations requiring extensive calculations, validations, or dependencies between entities.
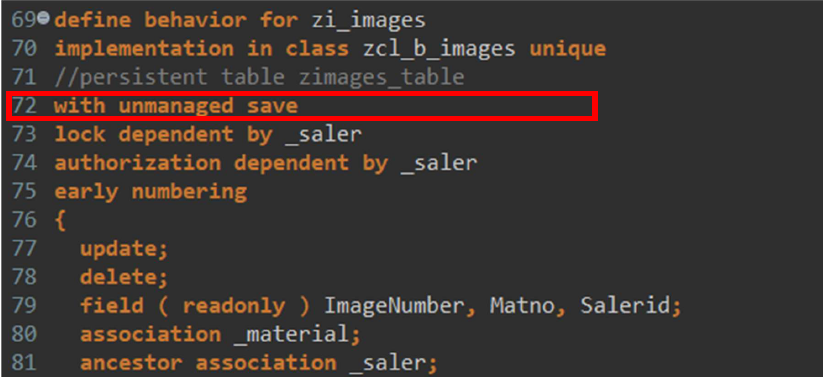
Steps to implement unmanage save.
Before that ensure persistence, table is not specified, as unmanaged save implementation cannot have persistence table specified to it.
Step 1: Include the unmanaged save keywords for all nodes where unmanaged behavior is required.
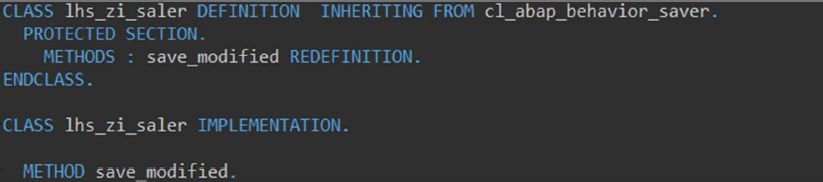
Step 2: Redefine method save_modified in Saver Local class implementation level.
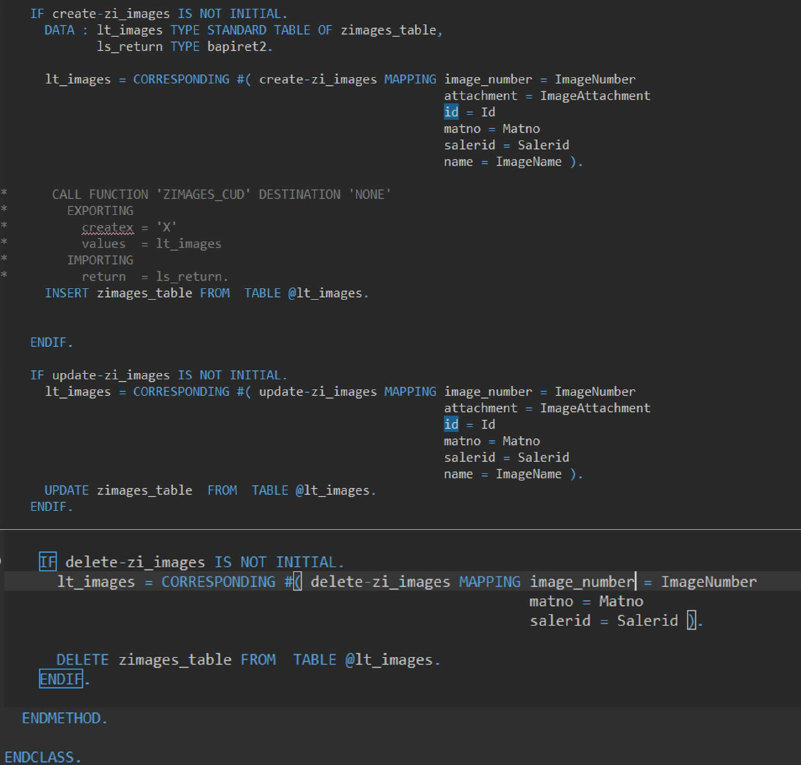
In this way we can implement the Unmanaged Save Sequence.