Inheritance allows one class to reuse the code from another class. In SAP ABAP, this helps in building modular, reusable, and maintainable programs.
Use of Inheritance in SAP
| Purpose | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Code Reusability | You don’t need to rewrite common logic; it can be inherited from a base class. |
| Standardization | Common functionality can be centralized in a superclass and reused. |
| Simplifies Maintenance | Changes in the parent class reflect automatically in all child classes. |
| Extensibility | Child classes can add or override methods to provide specific functionality. |
| Polymorphism Support | You can treat objects of different subclasses uniformly using references. |
Types of Inheritance in SAP ABAP
- Single Inheritance – A subclass inherits from only one parent class.
- No Multiple Inheritance – SAP ABAP does not support multiple inheritance, but it allows interfaces for similar functionality.
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
*& Report ZREP_LCLCLASS
*&
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
*&
*&
*&---------------------------------------------------------------------*
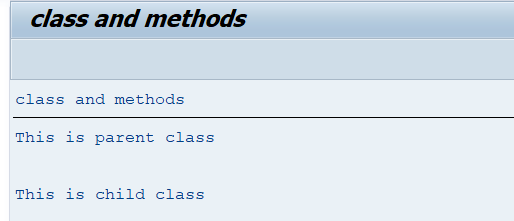
REPORT zrep_lclclass.
CLASS parent_class DEFINITION.
PUBLIC SECTION.
METHODS: display.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS parent_class IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD display.
WRITE: 'This is parent class'.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS child_class DEFINITION INHERITING FROM parent_class.
PUBLIC SECTION.
METHODS: show.
ENDCLASS.
CLASS child_class IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD show.
WRITE: 'This is child class'.
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
START-OF-SELECTION.
DATA obj TYPE REF TO child_class.
CREATE OBJECT obj.
obj->display( ). "Inherited method
skip 2.
obj->show( ). "Own method Output: