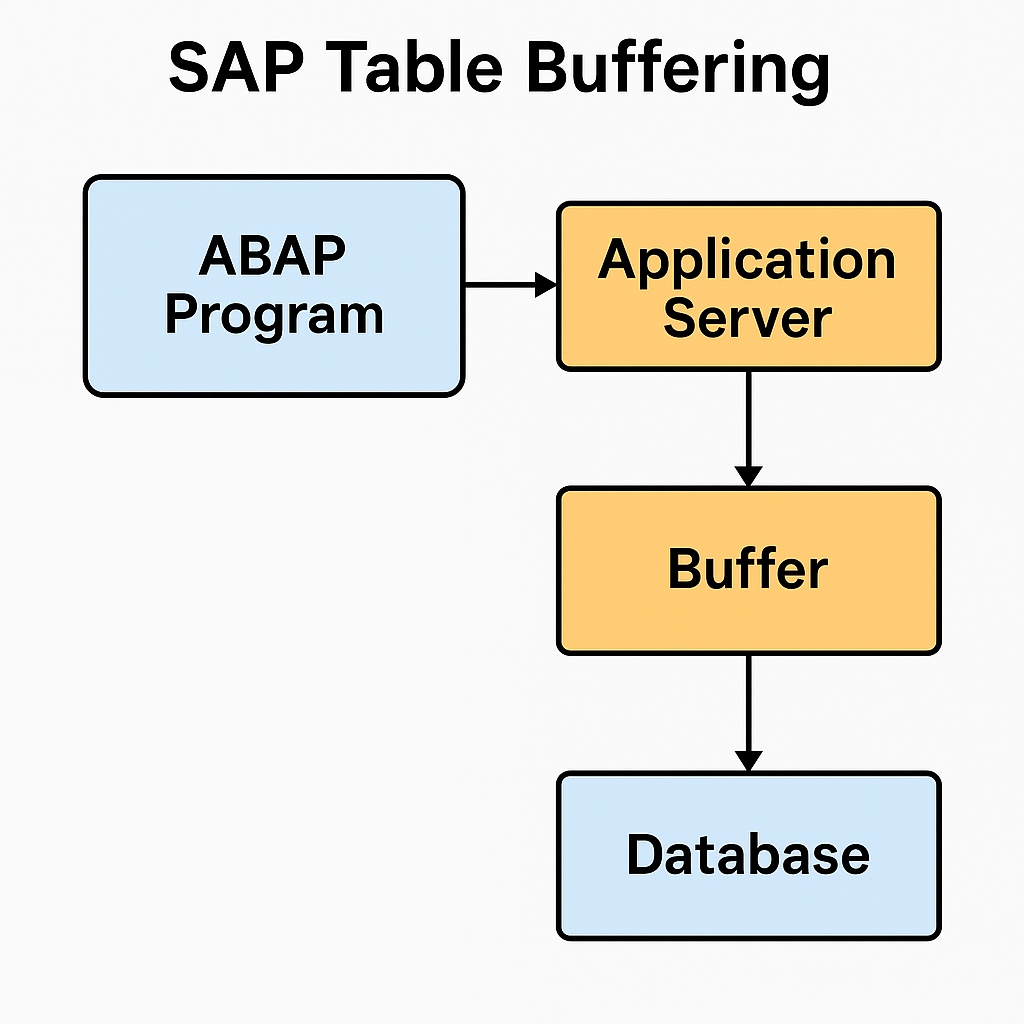
Buffering in SAP refers to storing table data in application server memory to reduce repeated database access. It enhances performance by retrieving frequently accessed data from memory instead of querying the database every time.
Why Buffer Tables?
- Speeds up data access (less DB load)
- Reduces network and database traffic
- Improves scalability for read-intensive operations
Buffering Applies Only to:
- Transparent tables
- That are client-dependent or have primary keys
- Typically read-intensive and rarely updated
You can check or set this in SE11 → Technical Settings.
Types of Buffering in SAP:
| Type of Buffering | Description |
|---|---|
| Single Record Buffering | Caches individual records (rows) based on primary key. Useful for tables where only one row is accessed at a time. |
| Generic Area Buffering | Caches subsets of records sharing a part of the key (a generic key). For example, buffer all rows for a specific country code. |
| Full Buffering | Loads the entire table into memory the first time it’s accessed. Best for small, static tables (e.g., customizing tables). |
Buffering Options in SE11:
You can configure table buffering under:
SE11 → Display Table → Technical Settings
Options:
- Buffering allowed / not allowed
- Buffering type (Full / Generic / Single Record)
- Generic key fields (for generic buffering)
When NOT to Use Buffering:
- Tables with frequent updates (e.g., transactional tables like
BKPF,BSEG) - Large tables that would consume too much memory
- Tables with high write/read concurrency